Waterjet Foam Cutting: The Ultimate Guide to Precision and Efficiency
In the realms of manufacturing, prototyping, and artistic creation, the quest for a cutting method that combines precision, versatility, and material integrity is never-ending. When it comes to cutting foam materials—a task notoriously tricky due to their delicate and often fragile nature—waterjet foam cutting emerges as a superior solution. Unlike thermal methods that can melt, burn, or release toxic fumes, waterjet foam cutting uses a high-pressure stream of water to achieve clean, precise, and stress-free cuts. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the world of waterjet foam cutting, exploring its fundamental principles, unparalleled advantages, diverse applications, key operational considerations, and how it compares to other cutting technologies. Whether you are in aerospace, packaging, or set design, understanding waterjet foam cutting could revolutionize your fabrication process.
What is Waterjet Foam Cutting? The Core Principles
Waterjet foam cutting is a subtractive manufacturing process that uses a highly pressurized stream of water, typically without abrasives, to slice through various types of foam materials. The core of this technology lies in its simplicity and effectiveness. A high-pressure pump, often intensifier or direct-drive type, pressurizes water to levels ranging from 30,000 to 90,000 pounds per square inch (psi). This pressurized water is then forced through a small orifice, usually made of sapphire or diamond, creating a coherent, supersonic jet capable of cutting through soft materials with remarkable accuracy.
The term “waterjet foam” specifically highlights the application of this technology on foam substrates. Unlike cutting metals or ceramics, which require the addition of abrasive garnet to the water stream, cutting foam typically utilizes a pure waterjet. This is because foams are soft materials; the sheer kinetic energy of the high-velocity water stream is sufficient to erode the material cleanly. The process is controlled by a Computer Numerical Control (CNC) system, which guides the cutting head along the X, Y, and Z axes based on a digital design file (e.g., DXF or DWG). This ensures extreme precision, allowing for the creation of complex shapes and patterns that would be difficult, if not impossible, to achieve with manual methods.
Why Choose Waterjet Technology for Foam? The Unmatched Advantages
The decision to use a waterjet foam cutting system is driven by a host of significant benefits that directly address the challenges of working with foam materials.
Cold Cutting Process: The most significant advantage. Waterjet foam cutting is a cold process. It generates no heat, eliminating any risk of melting, burning, or thermal distortion. This preserves the foam’s original cellular structure and physical properties, which is critical for materials like polystyrene or polyurethane that are highly sensitive to temperature.
Exceptional Precision and Complex Geometries: The CNC-guided water stream can achieve incredibly intricate cuts with tight tolerances (±0.005 inches is common). This allows for the production of complex patterns, sharp corners, and fine details that are essential in industries like aerospace for custom insulation or in design for intricate architectural models.
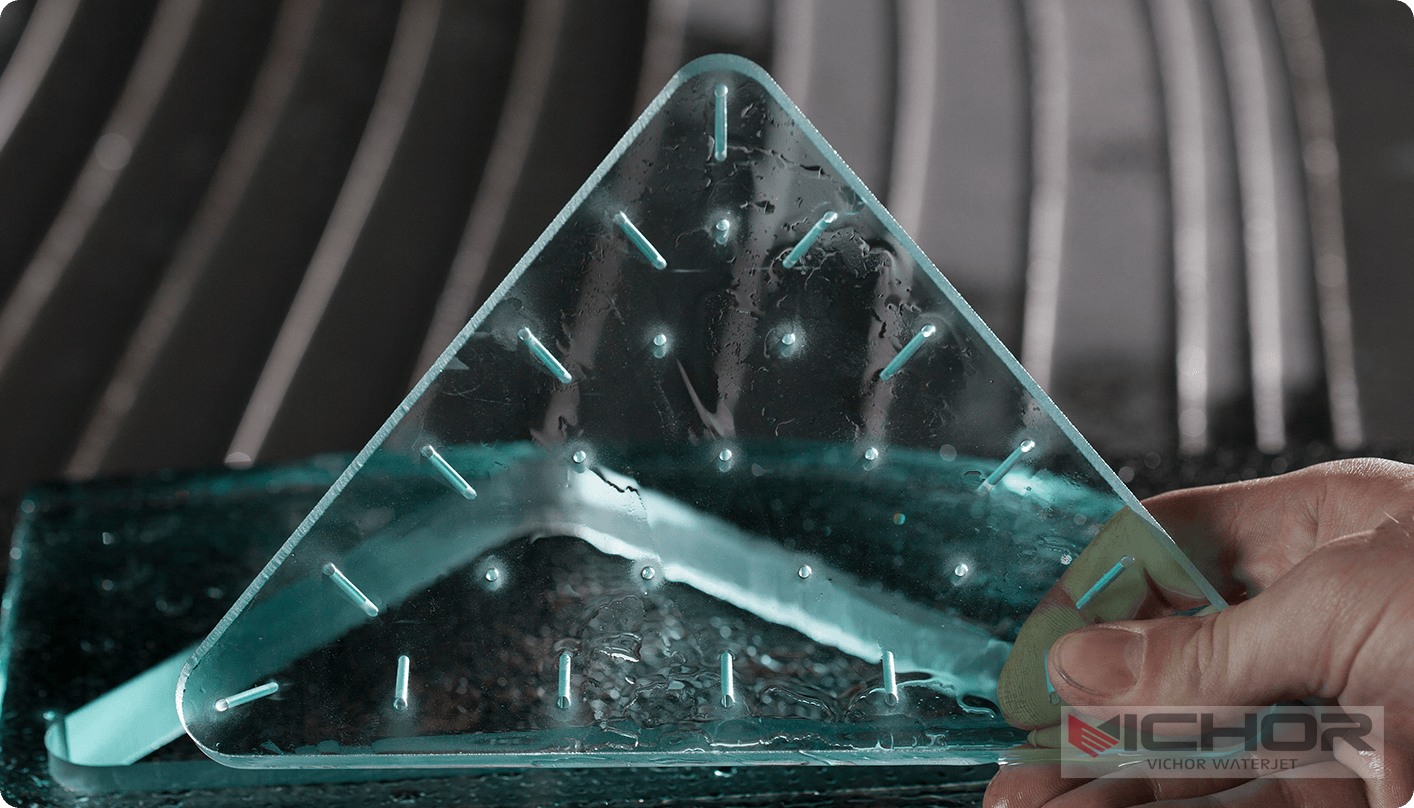
No Mechanical Stress: Unlike blade-based cutting tools (e.g., knives, saws), a waterjet exerts no mechanical force on the foam. This prevents compression, tearing, delamination, or the creation of dust and debris. The foam retains its original shape and density right up to the cut edge.
Material Versatility: A waterjet foam cutter can handle a vast array of foam types and densities without requiring tool changes. From soft, flexible open-cell foams to rigid, high-density closed-cell foams, the same machine can cut them all. Common materials include:
Polyurethane Foam (PU)
Polystyrene Foam (EPS and XPS)
Polyethylene Foam (PE)
Polypropylene Foam (PP)
Memory Foam
Foam Rubbers
Composite foam cores
Environmentally Friendly and Safe: The process uses only water and a tiny amount of electricity. It produces no hazardous fumes or vapors, which are a common byproduct of hot-wire or laser cutting certain foams. The water can often be filtered and recycled in a closed-loop system, minimizing waste.
Speed and Efficiency: For most foam applications, waterjet cutting is remarkably fast. The ability to nest parts closely together on a single sheet of material maximizes yield and minimizes waste, leading to lower material costs and higher overall efficiency.
Diverse Applications of Waterjet Foam Cutting Across Industries
The unique benefits of waterjet foam cutting have led to its adoption in a wide spectrum of industries.
Aerospace and Aviation: Used to precisely cut custom insulation panels, gaskets, and protective packaging for sensitive components. The ability to create complex shapes ensures a perfect fit within the tight confines of an aircraft’s structure.
Automotive: Essential for crafting interior components like headliners, seat cushions, armrests, and soundproofing materials. Prototyping new car interiors heavily relies on the precision of waterjet foam cutting.
Packaging: Ideal for producing custom protective foam inserts for high-value products like electronics, medical devices, and musical instruments. These inserts provide superior cushioning and a premium unboxing experience.
Construction and Architecture: Used for creating detailed architectural models, as well as cutting insulation boards (XPS, EPS) to specific shapes for unique building applications.
Arts, Entertainment, and Props: The technology is a favorite among sculptors, set designers, and prop makers. It can effortlessly transform large blocks of foam into intricate sculptures, thematic props, and detailed set pieces for film, theater, and theme parks.
Medical and Orthotics: For manufacturing custom medical cushions, prosthetics liners, and supportive padding that require a perfect fit for patient comfort and care.
Marine Industry: Used in the fabrication of flotation devices and insulation for boats.
Key Operational Considerations for Waterjet Foam Cutting
While highly effective, achieving optimal results with waterjet foam cutting requires attention to several key parameters:
Pressure and Flow Rate: Foam cutting requires lower water pressure compared to metals. Typically, pressures between 30,000 and 50,000 psi are sufficient. The flow rate must be calibrated to the foam’s density to ensure a clean cut without oversaturating the material.
Orifice Size and Nozzle Type: A smaller orifice (e.g., 0.004″ to 0.010″) is used for fine, detailed cuts in foam. Since abrasives are not needed, the nozzle assembly is simpler, reducing wear and operational costs.
Cutting Speed: The traverse speed of the cutting head is crucial. Too slow, and the water will saturate and potentially damage the foam. Too fast, and the jet won’t cut completely through. Finding the right speed for each material type and thickness is key.
Standoff Distance: This is the distance between the nozzle and the workpiece. Maintaining a consistent and correct standoff distance is vital for achieving uniform cut quality across the entire job.
Software and Nesting: Advanced CAD/CAM software is used to design parts and program the cutting path. Efficient nesting software helps arrange parts on the foam sheet to maximize material usage and minimize waste.
Waterjet Foam Cutting vs. Other Cutting Methods
How does waterjet foam cutting stack up against the competition?
vs. Hot Wire Cutting: Hot wire cutting is popular for foam but has limitations. It can only cut straight lines or very simple curves in a single plane and produces toxic fumes when cutting certain foams. Waterjet foam cutting offers full 2D and 3D capability, no fumes, and no risk of heat-related defects.
vs. Laser Cutting: Lasers can be precise but use heat, which melts the edges of foam, creating a hardened, often undesirable finish. They also pose a significant fire risk and fume hazard. Waterjet is a much safer and cleaner cold process.
vs. Blade Cutting/Knives: Manual or CNC blade cutting can crush and tear foam, especially softer varieties. It requires frequent blade changes, generates dust, and struggles with complex geometries. Waterjet is contactless and stress-free.
vs. Die Cutting: Dies are expensive and time-consuming to create, making them unsuitable for prototyping or low-volume production. Waterjet foam cutting requires no tooling, making it perfect for one-off pieces and short runs.
Maintaining Your Waterjet Foam Cutting System
Maintenance for a pure waterjet foam system (without abrasives) is relatively straightforward:
Regular Inspection: Check and replace the waterjet orifice and other seals as needed to maintain cutting pressure and quality.
Water Quality: Use deionized or filtered water to prevent mineral deposits from clogging the intricate parts of the high-pressure system.
Pump Maintenance: Follow the manufacturer’s schedule for maintaining the high-pressure pump, which is the heart of the system.
Table and Components: Keep the machine’s rails, drives, and catcher tank clean to ensure smooth operation and accuracy.
Waterjet foam cutting represents a perfect marriage of technology and material science. It solves the inherent challenges of cutting delicate, heat-sensitive foam materials by providing a cold, precise, and incredibly versatile solution. Its ability to produce stress-free, intricate cuts without compromising material integrity or operator safety makes it an indispensable tool across countless industries. As technology advances, making systems more efficient and user-friendly, the adoption of waterjet foam cutting is poised to grow even further, continuing to unlock new possibilities in design and manufacturing. For anyone looking to elevate their foam fabrication process, investing in waterjet technology is a clear and compelling choice.
continue reading
Related Posts
- 1077 words5.4 min read
- 1175 words5.9 min read
- 1255 words6.3 min read


